Overview
Bradford Assays are a widely used method for protein quantification in the field of biochemistry. It’s common and sensitive technique employed to determine the concentration of proteins in a sample. This colorimetric (numeric measurement of color) assay relies on the binding of Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye (a common type of dye) to proteins, resulting in a color change that can be measured and correlated to the protein concentration. Bradford Assays provide researchers with a quick and reliable method to quantify the amount of protein in a given sample. It is particularly useful in protein purification, protein expression studies, and protein quantification in various biological and biochemical experiments. They find applications in numerous fields, including biochemistry, molecular biology, proteomics, and pharmaceutical research. They are vital in protein purification workflows, assessing protein yield, and determining protein concentrations for downstream applications.
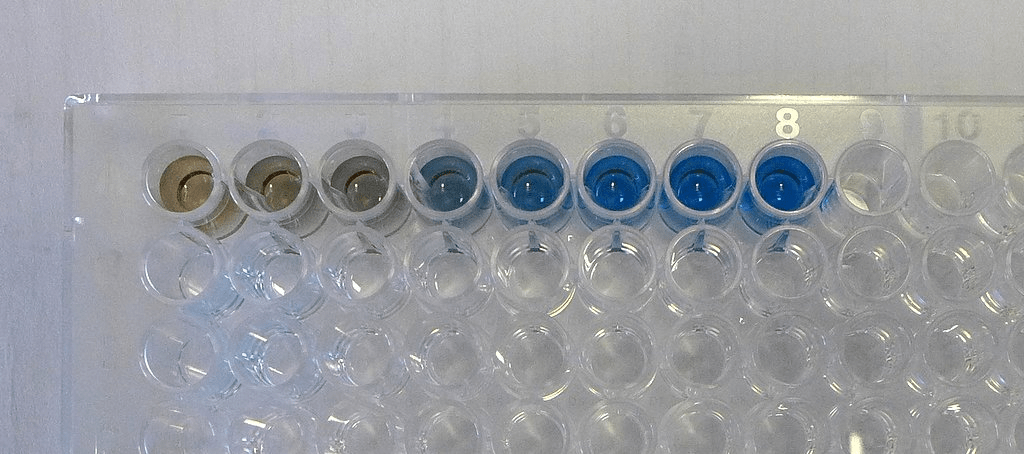
Materials Required for Bradford Assays:
To perform Bradford Assays, you’ll need several key components:
- Protein Sample: The solution containing the protein of interest that needs to be quantified.
- Bradford Reagent: The Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye solution, which binds to proteins and undergoes a color change upon binding.
- Spectrophotometer or Plate Reader: To measure the absorbance of the sample at specific wavelengths.
- Microplate or Cuvettes: Containers to hold the sample and reagents during the assay.
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Standard: A known concentration of BSA protein used to create a standard curve for protein quantification.
Basic Steps in Bradford Assays:
Here’s a simplified outline of the Bradford Assay process:
- Prepare Standard Curve: Prepare a series of known concentrations of BSA (standard) and measure their absorbance at a specific wavelength using the spectrophotometer. This data will be used to create a standard curve relating absorbance to protein concentration.
- Prepare Sample: Dilute the protein sample to be quantified to ensure it falls within the linear range of the standard curve.
- Add Bradford Reagent: Mix the sample with the Bradford reagent, allowing the dye to bind to the proteins.
- Incubation: Incubate the sample and Bradford reagent mixture for a specific period to allow sufficient color development.
- Measure Absorbance: Measure the absorbance of the sample at the appropriate wavelength using the spectrophotometer or plate reader.
- Calculate Protein Concentration: Use the standard curve to correlate the absorbance value of the sample with the corresponding protein concentration.
Bradford Assays offer a simple and accurate method for protein quantification, enabling researchers to analyze and compare protein concentrations across various samples. This technique plays a crucial role in protein-related research, facilitating the understanding of cellular processes, disease mechanisms, and the development of therapeutic interventions.
