What is the study of biology?
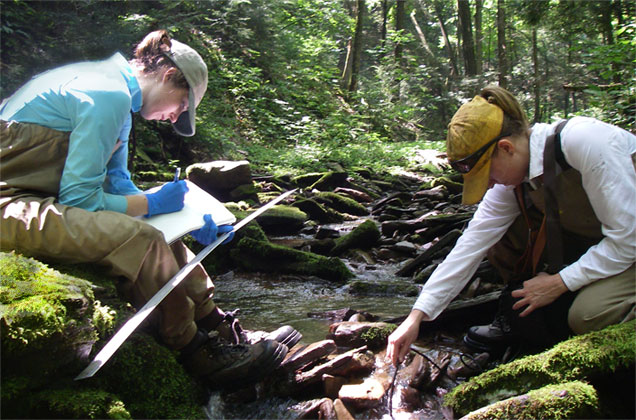
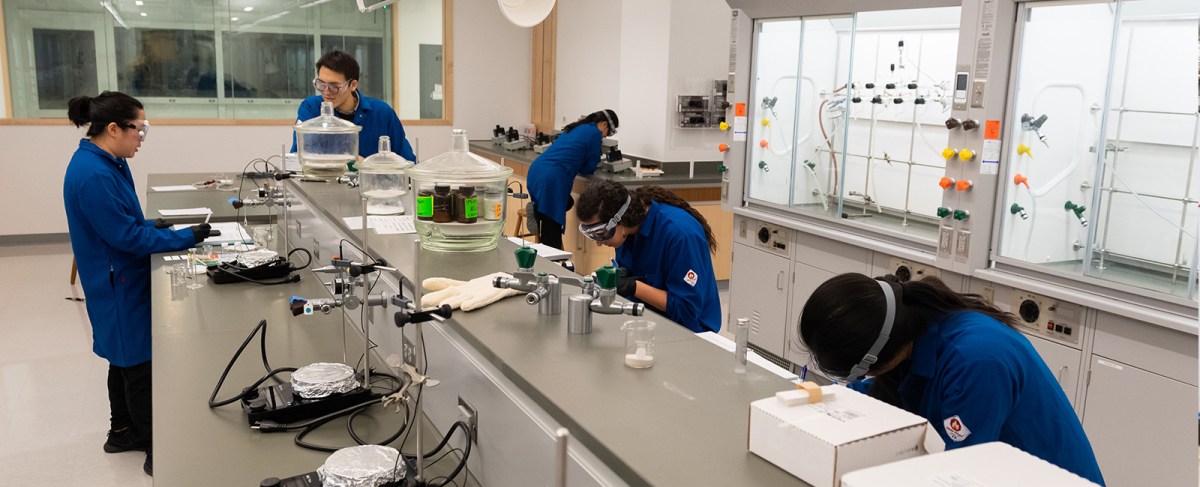
Biology is the scientific exploration of life and living organisms. Biology examines the processes and structures that sustain life, including genetics, ecology, physiology, microbiology, molecular biology, and evolutionary biology, just to name a few. Geneticists study the inheritance and expression of genes, seeking to understand how traits are passed down through generations. Ecologists investigate the intricate relationships between organisms and their environments, delving into ecosystems, biodiversity, and the interdependence of species. Physiologists focus on the mechanisms and functions that underlie the physiological processes of living organisms, spanning from cellular to systemic levels. Microbiologists explore the diverse world of microorganisms, ranging from bacteria and viruses to fungi and protists, unveiling their impact on health, disease, ecological systems, and so on. Each subtopic of biology studies a very small aspect of life, and they are all interconnected with each other.
Some notable figures
- Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, expounded in his seminal work “On the Origin of Species,” revolutionized the understanding of life’s history and diversity.
- Gregor Mendel, known as the “father of modern genetics,” conducted pioneering studies on pea plants, establishing the principles of inheritance that form the foundation of genetics.
- Rosalind Franklin’s crucial work on X-ray crystallography played an essential role in the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA by Watson and Crick.
- Jane Goodall’s groundbreaking research on chimpanzees provided profound insights into the behavior and social structure of our closest living relatives.
Some notable breakthroughs
- In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick unraveled the double helix structure of DNA, opening the doors to the molecular understanding of genetics and inheritance. This breakthrough laid the foundation for modern molecular biology and biotechnology, shaping fields like genomics and genetic engineering. In recent years, the development of CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology has sparked a revolution in genetic manipulation, enabling precise modifications to DNA with far-reaching implications for medicine and agriculture.
- The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, marked a milestone in biology, revealing the complete sequence of the human genome and fostering advances in personalized medicine and the study of genetic diseases.
What does it take?
Conducting biology research requires a diverse array of resources. Laboratories equipped with advanced instruments and technologies are essential for conducting experiments and analyses. Researchers often work with biological specimens, ranging from microorganisms and cell cultures to tissue samples and model organisms. Access to scientific literature, databases, and computational resources is vital for staying on top of current research and analyzing complex datasets.